
The SS Adriatic, last of the Big Four class, was the first ocean liner to provide a Turkish baths suite for the use of its passengers. The White Star Line was proud of its 'notable innovations', and made special mention of the Turkish baths in most of its publicity.1
It is now long since this ancient class of bathing was introduced into this country, and it has since undergone many extensions in style and method. Now it is interesting as well as significant to find that in the most popular vessel on the Atlantic Turkish Baths have been provided for the advantage of passengers. They consist of the usual hot, temperate and cooling-rooms, with shampooing rooms, a plunge bath, and massage couches. It is likewise worthy of remark that three electric baths have been provided.
The various areas of the bath were well laid out and, given that the Adriatic was the first liner to provide one, it must be assumed that the White Star Line sought advice from an experienced Turkish bath designer.



Cooling-room on the SS Adriatic: the launch; the early 1920s; 1928
The arrangement of the facilities on the later Titanic and Olympic liners was not as satisfactory, and it may be that by this time the company felt they no longer needed such advice, not realising that layout is absolutely critical to the optimal effectiveness of a Turkish bath.

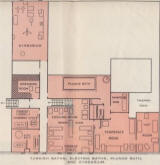
The SS Adriatic Turkish baths: at the launch, and after the 1928 refit
That the original 1907 design (above left) was successful may be deduced from the fact that there were so few changes made, either when the ship was refurbished after the 1914-18 War, or when it was converted to Cabin Class in 1928 (plan above right)—more clearly seen on the enlarged version of the plans.
 The main changes were: the replacement of one of the electric bath
rooms by a dressing room and (not labelled on the plan) a room for the
two Turkish bath attendants; the shared use of another one by a chiropodist; and the addition of curtains round some of the loungers. Otherwise, apart from a more sophisticated weighing chair and a larger dressing table, all that can be detected
are a few minor re-arrangements of the furniture.
The main changes were: the replacement of one of the electric bath
rooms by a dressing room and (not labelled on the plan) a room for the
two Turkish bath attendants; the shared use of another one by a chiropodist; and the addition of curtains round some of the loungers. Otherwise, apart from a more sophisticated weighing chair and a larger dressing table, all that can be detected
are a few minor re-arrangements of the furniture.
The Turkish bath was not only publicised in the company's brochures but also on their souvenirs.

Passengers could, for example, purchase a tin of biscuits made by the long-established firm of Carr & Co Ltd of Carlisle. This was decorated with a large picture of the ship on the lid and, displayed round the edge, four vignettes of scenes on board.
The wooden chair, seemingly mounted on top of a table, is the new weighing machine (more clearly seen in the enlarged images) which enabled bathers to check their weight before and after a Turkish bath.
Tickets for the Turkish or electric baths had to be purchased at the ship's enquiry desk. Either type of bath cost five shillings and sixpence, or one dollar 25 cents.2
It is interesting to see what changes were made after the liner was converted to Cabin Class, enabling less wealthy passengers (considered slightly 'lower class'?) to use the baths.
The provision of curtains round some of the loungers in the cooling-room has already been mentioned. The hours set aside for use by men and women also changed. When the boat first sailed, men were able to use the Turkish baths early in the morning from six till eight o'clock, and then again in the afternoon from two till six—a total of six hours per day. The afternoons from two till six o'clock were set aside for women—allowing them only four hours per day.2
But after the liner was converted, the early morning bath was no longer available. Women used the baths for three hours in the morning, and men for five hours in the afternoon and early evening.
What we do not know is whether the new hours reflected experience of past usage, or whether they were designed to make staffing requirements simpler so as to cut costs.
What is beyond doubt is that the White Star Line pioneered the inclusion of Turkish baths (and also, incidentally, swimming pools) on great ocean liners. In doing so, they set a precedent not only for their own later ships, but also for those of other shipping lines, including Cunard, with which it merged in 1934. In providing Turkish baths on the ss Adriatic, they set the pattern for the provision of sauna, steam room, and health spa on today's cruise liners worldwide.